Choose another country or region to see content specific to your location
Nurturing a Culture of Compliance: SEBI’s Role in ESG Implementation and the Transformative Power of LegalTech
November 25, 2023

In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, fostering a culture of compliance is critical, particularly when it comes to addressing each of the pillars of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG). The increasing importance of ESG factors is driving a new urgency in integrating these principles into the core of corporate culture whereas the ESG framework itself is relatively new; tracing its roots back to the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investing (UNPRI), initiated in 2006.
The ESG methodology is designed to embed within a company the multiple strains of environmental responsibility, social consciousness, and ethical governance. Given the demanding objectives of each of its components, achieving excellence in ESG requires a collective effort where the whole company contributes to and tracks achievements in each of the three areas.
What is the Need for ESG in India?
India faces significant environmental issues, including pollution of the environment, the challenges of providing clean drinking water and the repercussions of climate change. The country also contends with substantial social issues such as poverty, inequality, discrimination, workplace sexual harassment and instances of human rights violations. Other obstacles such as corruption, over-regulation, and corporate governance pose more challenges. Accordingly, there is an increasing need for companies to embed strong governance practices to adeptly navigate these risks.
On the investment side, three pivotal elements are driving ESG momentum in India.
- India’s pledge to achieve the Net Zero target by 2070 requires a capital investment of around USD 8-10 trillion over the next 50 years. More than twelve companies, including Reliance Industries Ltd, Vedanta Ltd, ITC Limited, JSW Energy, HDFC Bank, etc have committed to achieve carbon neutrality in the future.
- SEBI’s directives on Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR) have provided regulatory impetus for listed entities to embed sustainable practices in their businesses.
- The third factor is the increasing emphasis being placed on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in assessing a company’s achievements and its capacity to attract capital.
Enforcement of ESG in India
In India, the regulatory structure overseeing ESG does not have the benefit of a unified legislative base. Instead, a multitude of laws collectively referred to as the ‘ESG framework’ will govern ESG-related aspects affecting the activities of corporate entities in the country. The regulatory structure includes legislation as diverse as:
- environmental protection (eg, the Environment Protection Act, 1986);
- employee benefits (eg, the Factories Act, 1948; bonus and gratuity laws); and
- corporate governance (eg, the Companies Act, 2013; the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Act, 1992).
In ESG-related matters, adjudicative bodies with investigative powers are responsible for implementing and enforcing the obligations of Indian companies thereunder. These enforcement bodies have the authority to:
- request information;
- undertake investigations; and
- adjudicate upon any resulting non-compliance.
Privately held companies are increasingly showing a keen interest in adhering to global ESG standards, aiming to attract foreign investors who prioritize the sustainability of their investments. ITC Limited, a prominent tobacco and consumer goods manufacturer and hotel operator joined this trend by pledging to certify all its factories and hotels in high-water stress areas to the International Water Stewardship Standard, a recognized global benchmark. Noteworthy Indian companies like Tech Mahindra, Infosys, and Wipro, along with major players in the fast-moving consumer goods sector like Nestlé India, have similarly committed to sustainability objectives. Their goals include reducing energy and resource consumption in manufacturing facilities and ambitious plans to achieve complete recycling or reuse of packaging materials within the next decade.
ESG Regulations in India and the Role of SEBI
In India, there has been a notable increase in the prominence of ESG regulations. This surge is propelled by a growing awareness of ESG-related risks and opportunities among investors.
SEBI, the regulatory authority for the Indian securities market, has been actively championing ESG investing in the country through various initiatives. SEBI’s involvement in the implementation of ESG reflects a commitment to fostering sustainable and responsible business practices in India’s capital markets. By incorporating ESG considerations into the regulatory framework, SEBI contributes to the broader global movement towards ethical, socially responsible, and environmentally sustainable financial markets.
Here are some of the key areas of SEBI’s involvement in the implementation of ESG:
- Mandating ESG Disclosures: SEBI has made it mandatory for listed companies to disclose their ESG-related initiatives and performance in their annual reports. This requirement ensures transparency and accountability, compelling companies to provide stakeholders with comprehensive information on their environmental, social, and governance practices. In 2012, SEBI released a guidance note on ESG disclosure, advising that companies listed on Indian stock exchanges should disclose their ESG performance in their annual reports.
- SEBI Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements (LODR): SEBI has incorporated ESG-related disclosures into the Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements (LODR) for listed entities via Regulation 34 (2).
- Guidance on Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting (BRSR): In 2021, SEBI has guided Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting, outlining the framework for companies to report on their ESG performance. This framework assists companies in aligning their business strategies with ESG principles, fostering a culture of responsible and sustainable business operations. It seeks disclosure from listed entities on 9 principles of National Guidelines on Responsible Business Conduct (NGBRCs). SEBI is actively monitoring these disclosures and has introduced revisions in 2023.
- Green Bonds Framework: SEBI has introduced a Green Bonds Framework to promote environmentally sustainable projects after the introduction of the same by the government of India in the 2022-23 budget. This framework establishes guidelines for companies looking to raise funds through green bonds, ensuring that the proceeds are utilized for projects with positive environmental impacts.
- Engagement with Stakeholders: SEBI actively engages with stakeholders, including investors, companies, and industry bodies, to promote awareness and understanding of ESG principles. This engagement fosters a collaborative approach toward the effective implementation of ESG practices across the financial markets.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: SEBI has undertaken capacity-building initiatives to enhance the understanding of ESG concepts among market participants. These initiatives include workshops, seminars, and collaborations with industry experts to facilitate the adoption of ESG best practices.
- Asset Management Companies (AMCs): The business responsibility and sustainability reporting (BRSR) seeks disclosures from listed entities on their performance. In 2020 SEBI mandated that AMCs establish a framework for ESG investing. This involves defining the criteria for selecting securities based on ESG factors and integrating these considerations into the investment decision-making process.
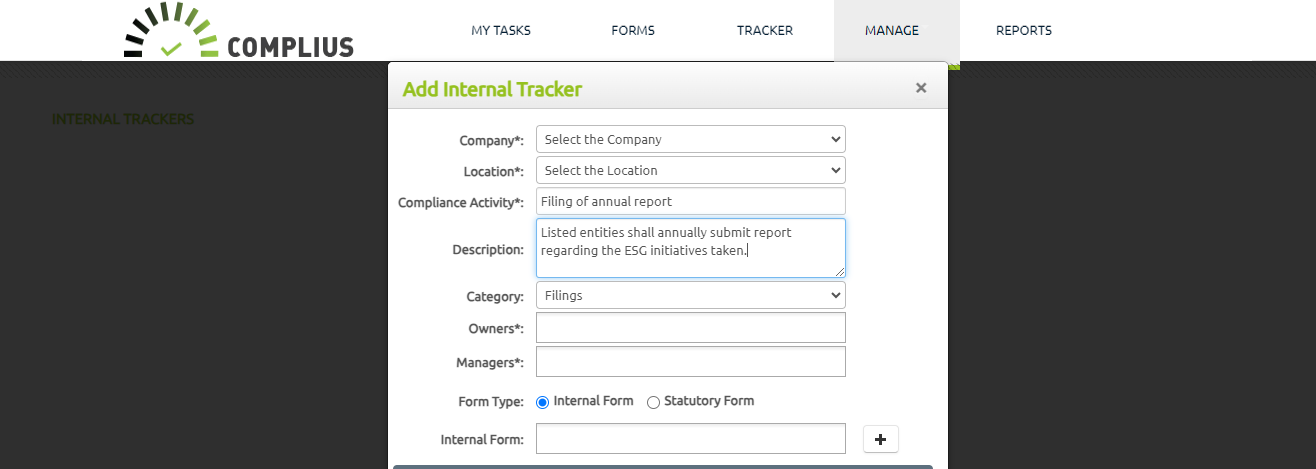
How does Quant Legal-Tech’s Complius® help you manage ESG Compliance Activities?
In the pursuit of incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles seamlessly into their core operations, businesses are turning to technology as a formidable ally to instill a culture of compliance. Quant Legal-Tech’s compliance management tool, Complius®, emerges as a comprehensive solution addressing industry compliance requirements.
Complius® can contribute in several areas:
- Automated Compliance Monitoring: Complius® automates SEBI compliance tracking, keeping issuers updated.
- Data Management and Analysis: Legal Tech tools efficiently handle and analyze large volumes of ESG-related data, including environmental impact assessments, social responsibility metrics, and governance practices. This processing capability aids in making informed decisions aligned with ESG principles.
- Contract Management: ESG implementation often requires contractual commitments related to sustainability, ethical sourcing, and social responsibility which Complius® with advanced contract management features streamline contract creation, monitoring, and enforcement, ensuring ESG commitments are fulfilled.
- Blockchain for Transparency: Integrated into Legal Tech solutions, blockchain enhances transparency in supply chains, crucial for ESG initiatives. It ensures traceability and integrity, creating a transparent and tamper-proof record of ESG efforts.
- Due Diligence and Risk Assessment: Complius® can expedite due diligence related to ESG by automating risk assessments and analyzing potential legal, financial, and reputational risks, enabling informed decisions.
- Audit Trail and Compliance Verification: Maintains a transparent compliance history which can enhance accountability and maintain reliable records for audits.
- Deadline Tracking: Ensure timely filings and submissions.
- Data Analytics: Analyze compliance performance for improvements.
- Regulatory Alerts: Receive real-time SEBI regulation updates.
- Data Security: Ensure data privacy and security.
The complexity of ESG implementation, demands that every department in an organization, contribute to a matrix of reporting with Director-level oversight. Legal-tech solutions, such as Complius®, play a crucial role in simplifying this complexity, offering transparency into task ownership and execution. Complius® uniquely facilitates the maintenance of internal activities within an entity, contributing to the cultivation of a compliance-driven culture.
Conclusion
As India strides towards a future where ESG considerations are integral to corporate decision-making, SEBI’s role in fostering a culture of compliance is pivotal. Embracing LegalTech solutions further amplifies this effort, providing companies with the tools they need to seamlessly navigate the complexities of ESG implementation. By harnessing the power of technology, businesses can not only meet regulatory requirements but also contribute meaningfully to a sustainable and responsible corporate landscape.