Choose another country or region to see content specific to your location
Exploring Dark patterns and navigating its implications in Legal Tech
December 29, 2023

Introduction
Dark patterns, deceptive design tactics employed by websites and apps to manipulate user behaviour, are widespread across various online platforms, ranging from popular news websites to beloved food delivery apps. Often considered as deceptive advertising or unethical business practices, these tactics can be viewed as violations of consumer rights. Recognizing the need to address this issue, legislators have taken an approach by introducing the Guidelines for Prevention and Regulation of Dark Patterns in 2023, aiming to protect consumers and curb the prevalence of these manipulative practices.
Recently, in the case of Anil Kapoor Vs Simply Life India & Ors, while upholding the Personality Rights of the famous Bollywood Actor Anil Kapoor in an Interim Order, the use of Dark Patterns as a method of personality rights’ violation was presented to the Hon’ble Delhi High Court. Anil Kapoor’s legal battle to protect his personality rights highlighted the evolving challenges in the digital age, where dark patterns and deceptive practices can threaten an individual’s identity and reputation. The Hon’ble High Court of Delhi reinforced the importance of safeguarding personality rights in the face of technological advancements and deceptive online tactics. A significant development in Kapoor’s case led to the introduction of the ‘Prevention and Regulation of Dark Patterns 2023,’ proposed by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Government of India.
In the dynamic landscape of legal technology, staying at the forefront requires not only innovation but also a commitment to ethical considerations. The year 2023 signifies a pivotal moment for the legal tech industry as it grapples with the introduction of Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 and comprehensive guidelines focused on preventing and regulating dark patterns. These guidelines, geared towards promoting transparency and ethical practices. Embracing these standards becomes essential for legal tech entities to navigate a landscape increasingly shaped by ethical expectations and to build a foundation of trust with users.
History Behind Introduction of Guidelines for Prevention and Regulation of Dark Patterns, 2023
The introduction of regulations specifically targeting dark patterns reflects a response to the growing concerns about unethical design practices and the negative impact on user experience across various digital platforms. The history behind the introduction of dark patterns regulations is marked by a series of events and developments that highlighted the need for legislators to address these issues.
- Rise of Dark Patterns: Dark patterns have been present on the internet for quite some time, but their prevalence and sophistication increased with the growth of e-commerce and digital services which increased employing manipulative design techniques to influence user behaviour.
- Consumer Advocacy and Complaints: As users became more aware of manipulative design practices, consumer advocacy groups and individuals started raising concerns and filing complaints.
- High-Profile Cases and Scandals: Several high-profile cases and scandals drew public attention to the impact of dark patterns. Instances of companies using deceptive practices to manipulate users, especially in the areas of privacy and data consent, came under scrutiny. These cases contributed to a broader public awareness of the potential harm caused by dark patterns.
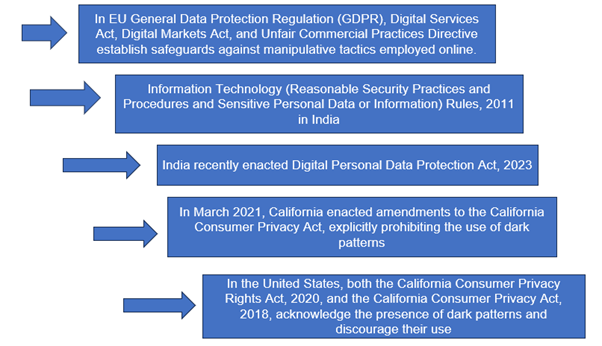
- Implementation of Data Protection Regulations in various jurisdictions: GDPR underscores the significance of informed consent and users’ rights concerning their personal data. In tandem, legislation such as the Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures and Sensitive Personal Data or Information) Rules, 2011 in India mandates obtaining informed consent from users before collecting sensitive personal data. Similarly, India’s recently enacted Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 emphasizes securing explicit consent from Data Principals before processing such information. There was a notable instance where the French Data Protection Act imposed an €8 million fine on Apple for collecting the identity of users that visited the App Store using the old iPhone operating system (version 14.6) for several purposes, including to personalize ads shown on the App Store. Apple was collecting such data by default, without obtaining users’ consent.

- Initiatives by Tech Advocates and Organizations: Technology advocates and organizations dedicated to digital ethics began pushing for clearer standards and regulations. They argued that voluntary codes of conduct were insufficient, and legally binding rules were necessary to curb the misuse of design patterns that harm user autonomy.
Cases to highlight the impact of Dark Patterns
Here are a few notable cases that highlight the impact of dark patterns:
- Facebook’s Privacy Settings (2018): Facebook has faced multiple controversies related to privacy where dark patterns were alleged to be a part of its interface design. In 2018, amidst the Cambridge Analytica scandal, it was revealed that Facebook’s privacy settings were intentionally designed to be confusing, making it challenging for users to control the visibility of their personal information. The incident led to increased public and regulatory scrutiny.
- Google’s Location Tracking (2018): In 2018, an investigation by the Associated Press revealed that Google’s Android devices continued to track users’ locations even when the location history setting was turned off. The design of the user interface was criticized for being misleading and not providing clear information about the extent of location tracking. Google subsequently updated its interface and settings.
- Zoom’s Dark Pattern Allegations (2020): Zoom, the video conferencing platform, faced criticism in 2020 for its design choices during the COVID-19 pandemic. Zoom was facing lawsuits that allege the company is illegally disclosing personal information to third parties. Apple was forced to step in and silently remove Zoom software from Macs last year after a serious security vulnerability let websites hijack Mac cameras.
Compliances of Dark Pattern Regulations for organizations
Dark patterns which need to be avoided as per guidelines includes an indicative and not exhaustive list which can be referred in Annexure I.
The compliances which all organizations need to comply to operate digitally are following: –
- Ensure that they are not using dark patterns by looking over their user interfaces and marketing materials.
- Get users express informed consent before collecting or using their personal information.
- Give consumers the option to view, update, and remove their personal information.
- Safeguard user information against unauthorised use, access, or disclosure.
- Customers should be taught how to spot dark patterns, and industry standards for dark pattern-free user interfaces should be developed.
- Maintain compliance, incorporate consent documentation or pop-up notifications on digital platforms.
- Provide personalised user experiences on digital platforms.
- Implementing encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security precautions can improve user interfaces.
- A system to guarantee the processed data is accurate, consistent, full, and correct.
Consequence of non-compliance
The penalty thresholds haven’t been clearly defined in the guidelines. There are no precise definitions of punishment criteria in the guidelines. Therefore, the Consumer Protection Act of 2019 would impose severe fines on any of the dark patterns mentioned in Annexure 1 of the guidelines.
Implications for the Legal Tech Industry
- Enhanced Trust and Credibility: Adherence to the guidelines will result in enhanced trust and credibility for legal tech providers. Users are more likely to engage with platforms that prioritize transparency and ethical practices, fostering a positive industry reputation.
- Legal Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Compliance with the guidelines is not a matter of ethical responsibility but also legal necessity. Failure to adhere to the prescribed standards may lead to legal consequences, including fines and reputational damage. Legal tech companies are now compelled to integrate these considerations into their business models and practices.
- Innovation in Ethical Design: These guidelines present an opportunity for legal tech companies to get involved in ethical design. By prioritizing user experience and ethical considerations, companies can distinguish themselves in a crowded market and attract users who value transparency and responsible technology use.
How can Quant Legal-Tech help you to avoid inclusion of dark patterns in Compliance Activities?
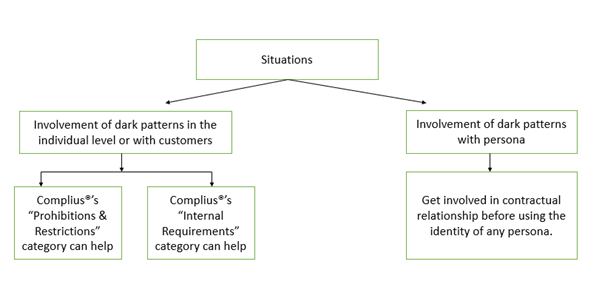
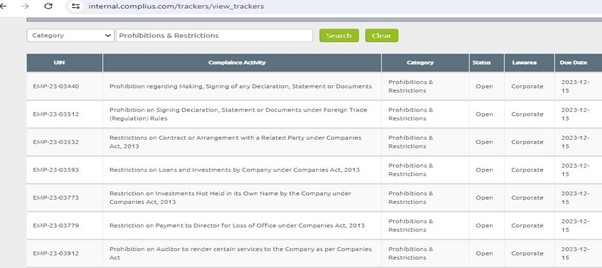
Complius® provides timely reminders of the various prohibitions and restrictions which relate to the use of dark patterns. This enables companies to build customized workflows which test for the presence of behaviour that may violate the new restrictions. Managers can also fine tune this methodology by building sub-tasks which must be completed before an activity can be approved.
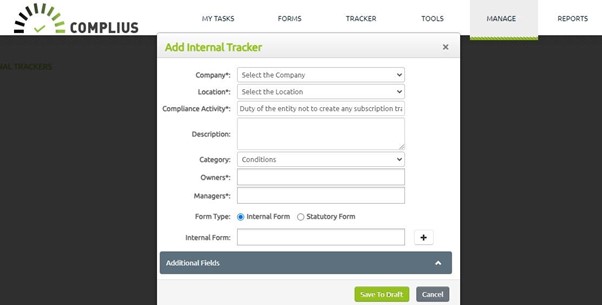
As the penalty thresholds have not been clearly defined in the guidelines, Complius® uniquely facilitates the maintenance of internal activities within an entity, contributing to the cultivation of a compliance-driven culture.
Conclusion
The Guidelines for Prevention and Regulation of Dark Patterns in 2023 mark a significant stride in steering the legal tech industry towards ethical practices and user protection. The introduction of these guidelines reflects a proactive involvement by legislators to address the rising concerns surrounding deceptive design tactics and their adverse impact on user experiences.
In this landscape, Quant Legal-Tech’s Complius® emerges as a valuable ally, offering practical assistance in creating checklists and fostering a compliance-driven culture within organizations. As the legal tech industry continues to evolve, these guidelines serve as a compass, guiding it towards a future where innovation is synonymous with responsibility and ethical integrity.