Choose another country or region to see content specific to your location
Corporate Governance
November 21, 2022

What is Corporate Governance?
The term “Corporate Governance” refers to the system of rules, practices, policies, and processes by which companies are governed. In essence, it entails weighing the interests of a company’s various stakeholders, including shareholders, senior management executives, customers, suppliers, financiers, the government, and the community.
The essential principles of Corporate Governance that must be followed are:-
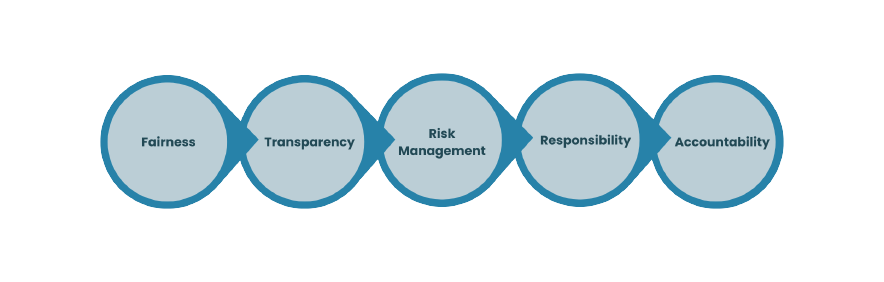
Corporate Governance is concerned with determining how to make effective strategic decisions. The board’s responsibilities include setting the company’s strategic goals, providing leadership to put them into action, supervising business management, and reporting to shareholders on their governance.
It is necessary for today’s market-oriented and globalized economy as Corporate Governance adds a normative or evaluative component to this process. In a nutshell, good governance refers to the institutional and political outcomes required to achieve developmental goals. The concept has grown in importance in recent years, emerging as a critical component for growth and long-term development. The extent to which it upholds human rights, including civil, cultural, economic, political, and social indicators, is the key measure of good governance.
Corporate Governance assures stakeholders that an organization fulfills its obligations to all its stakeholders, treats everyone with respect, and is transparent about its operations, finances, and actions. An institution’s devotion to incorporating good governance principles in all aspects of its operations and decision-making is a major indicator of its quality and excellence. It is widely acknowledged that failure to uphold these principles can hurt welfare, efficiency, and operational excellence, affecting organizations’ long-term success.
Corporate Governance– History in India
The 20th century witnessed the Indian economy’s glory due to liberalization, globalization, and privatization. Indian economy for the first time here was together with the world economy for a product, capital, and labor market and which resulted in a world of capitalization, corporate culture, business ethics which was found important for the existence of a corporation in the world marketplace. The organizational framework for corporate governance initiatives in India consists of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). In 1998, the CII unveiled India’s first code of corporate governance. Moreover, SEBI and the Ministry of Corporate Affairs have appointed many committees to modify the existing structure of Corporate Governance in India. They are,
Kumar Mangalam Birla Committee
N.R. Narayan Murthy Committee
Naresh Chandra Committee on Corporate Audit and Governance
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs had also set up a National Foundation for Corporate Governance (NFCG) in association with the CII, ICAI, and ICSI as a not-for-profit trust to provide a platform to deliberate on issues relating to good corporate governance, to sensitize corporate leaders on the importance of good corporate governance practices as well as to facilitate the exchange of experiences and ideas amongst corporate leaders, policymakers, regulators, law enforcing agencies and nongovernment organizations.
The Companies Act, 2013 guidelines on Corporate Governance
- Qualifications for Independent Directors along with the duties and guidelines for professional conduct.
- Mandatory appointment of one-woman director on the board of listed companies.
- Mandatory establishment of certain committees like Corporate Social Responsibility Committee, Audit Committee, Nomination, and Remuneration Committee, and Stakeholders Relationship Committee.
- Holding a minimum of four meetings of the Board of Directors every year in such a manner that not more than 120 days shall intervene between two consecutive meetings of the Board.
SEBI guidelines on Corporate Governance
- Minimum information to be placed before the board like operating plans and budgets, capital budgets, quarterly results, minutes of the meetings, information on recruitment and remuneration of senior officers, etc.,
- Compliance certificate by CEO and CFO.
- Role of the audit committee and review of information by an audit committee.
- Role of Nomination and Remuneration committee.
- Role of stakeholders’ relationship committee.
- Quarterly compliance report requirements.
- Disclosures with respect to the Corporate Governance report.